Connect Your GitHub Repository to AWS Securely Using OIDC
OpenID Connect (OIDC) enables GitHub Actions to authenticate with AWS without relying on long-lived credentials. By generating short-lived, temporary tokens for each workflow run, OIDC strengthens security and simplifies credential management, eliminating the need to store sensitive secrets in your repository.
Why Use OIDC with GitHub Actions and AWS?
OIDC is the most secure and recommended method for authenticating GitHub Actions with AWS. It removes the risk of exposing AWS access keys by replacing them with automatically generated, short-lived tokens. This approach minimizes credential exposure while ensuring seamless, secure access to AWS resources.
- Enhanced Security: Eliminates the need to store long-lived AWS access keys or secrets in your repository.
- Automation Token Rotation: Tokens are automatically generated and rotated for each workflow run, reducing the risk of credential leakage.
- Granular Access Control: You can define fine-grained permissions for each workflow or repository,ensuring the principle of least privilege.
Configure the OIDC Provider in AWS
To allow AWS to trust GitHub as an identity provider, you need to create an IAM OIDC identity provider in your AWS account.
Create the OIDC Provider
Navigate to IAM
Go to the IAM Console , select Identity providers, and click Add provider.
Configure the Provider details
- Provider type: Select OpenID Connect.
- Provider URL: Enter
https://token.actions.githubusercontent.com. - Audience: Enter
sts.amazonaws.com.
Click Add provider.
Create an IAM Role for GitHub Actions
Create a Role
Go to Roles and click Create role.
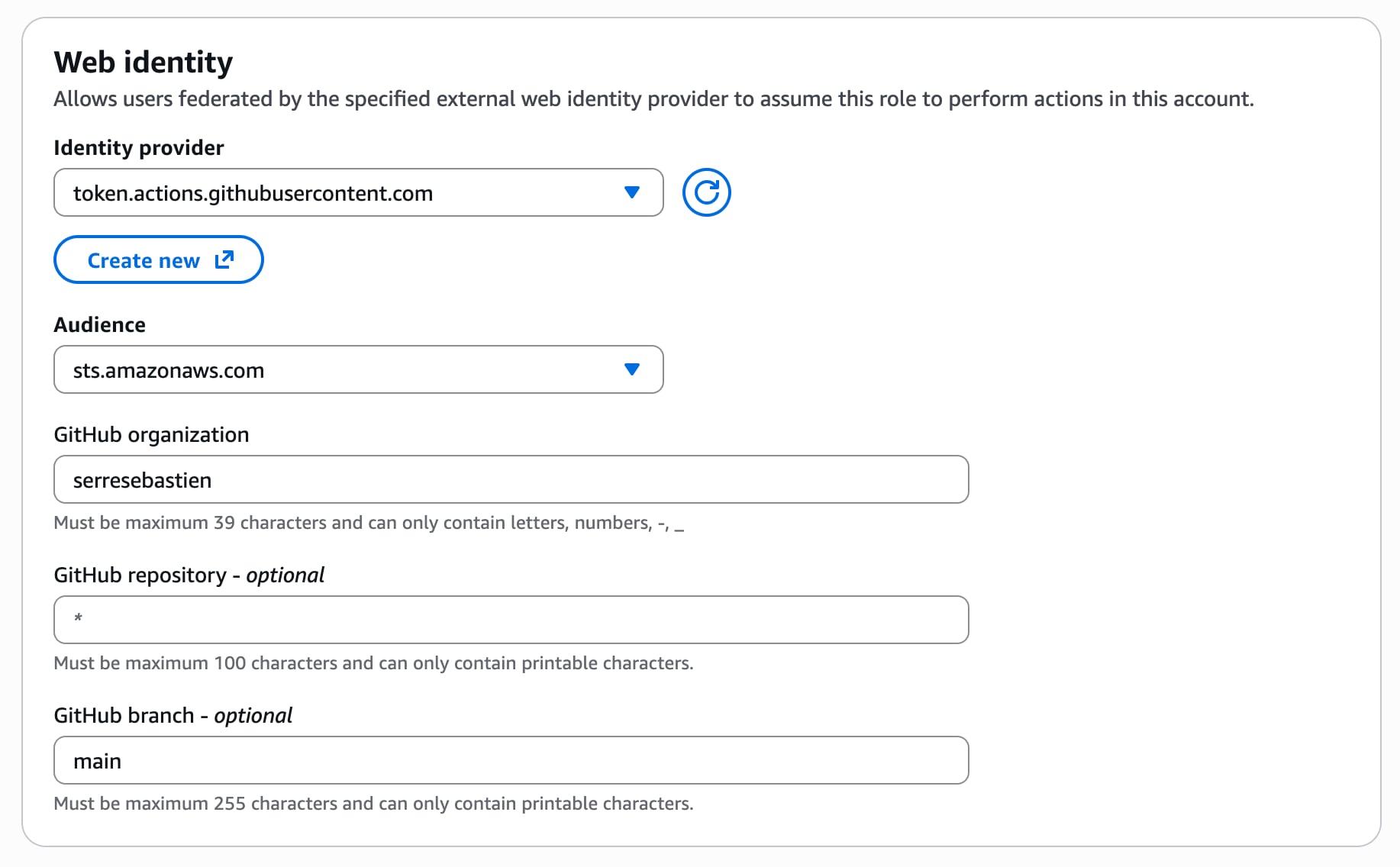
- Trusted entity type: Select Web identity.
- Identity provider: Choose the provider you just created (token.actions.githubusercontent.com).
- Audience: Select
sts.amazonaws.com. - GitHub repository: If you either want to allow only a specific repository or every repository of your account/organization (default
*for all repositories). - GitHub branch: If you either want to allow only a specific branch or every branch to be able to access your AWS account (default
*for all branches, I recommend to usemainto enforce least privilege).
Attach Permissions
Attach the necessary policies to the role (AdministratorAccess for temporary testing, or a custom policy with least-privilege permissions for production).
Review the Role
Restrict which GitHub repositories and branches can assume this role. I recommend you explicitly specify the branches you want to allow, main and dev for example. You should get a similar policy as below:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": "sts:AssumeRoleWithWebIdentity",
"Principal": {
"Federated": "arn:aws:iam::<ACCOUNT_ID>:oidc-provider/token.actions.githubusercontent.com"
},
"Condition": {
"StringEquals": {
"token.actions.githubusercontent.com:aud": "sts.amazonaws.com"
},
"StringLike": {
"token.actions.githubusercontent.com:sub": [
"<REPOSITORY>"
]
}
}
}
]
}
<ACCOUNT_ID> should be your AWS account ID and <REPOSITORY> the Github repository. The repository must be in the form repo:ORG-NAME/REPO-NAME:ref:refs:/heads/BRANCH or repo:ORG-NAME/REPO-NAME:* to allow any branch.Name and Create the Role
Name the role GitHubActionsRole and create it.
Create a GitHub Actions workflow
Once your AWS Account is set up, let's create a workflow file .github/workflows/deploy.yml in your repository as follows:
name: Verify AWS OIDC
on:
push:
branches:
- main
permissions:
id-token: write # This is required for GitHub to request a JWT
contents: read
jobs:
deploy:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Checkout code
uses: actions/checkout@v5
- name: Configure AWS credentials
uses: aws-actions/configure-aws-credentials@v4
with:
role-to-assume: arn:aws:iam::<ACCOUNT_ID>:role/GitHubActionsRole
aws-region: us-east-1
- name: Verify AWS identity
run: aws sts get-caller-identity
<ACCOUNT_ID> with your AWS account ID.aws-actions/configure-aws-credentials action handles the OIDC token exchange and configures the AWS CLI.Test the workflow
Commit and Push
Commit the workflow file to the main branch. The workflow will run automatically.
Check the Output
In the GitHub Actions log, you should see the output of aws sts get-caller-identity, confirming that the workflow has successfully assumed the IAM role previously created.
Best Practices
Now that you have successfully linked your AWS account to your GitHub repository, be sure to respect these best practices:
- Least Privilege: Always attach the minimum required permissions to the IAM role.
- Branch Protection: Use conditions to restrict which branches or tags can assume the role.
- Audit Logs: Monitor AWS CloudTrail and GitHub Actions logs for unusual activity.
Troubleshooting
If you encounter any issues when running your workflow, it might come from:
- Permission Errors: Ensure the IAM role has the correct trust policy and permissions.
- Workflow Failures: Check the GitHub Actions log for detailed error messages.
- Token Issues: Verify that the
id-token: writepermission is set and the OIDC provider is correctly configured in AWS.